How Steel Hot Rolling Mills Work
Steel is a versatile material that’s widely used due to its strength, durability, and flexibility. Its demand is expected to grow by about 2.2% to reach 1 881.4 Mt in 2023.
But before steel is used in various applications, it must undergo production. One of the ways to make steel is through hot rolling. Unlike unprocessed steel, hot-rolled steel displays greater workability and formability. This makes it easier to work with in consequent processing operations.
What Is Hot-Rolled Steel?
This form of steel is manufactured by heating it at extremely high temperatures and passing it through rolling mills machinery. The temperature used is usually above the material’s recrystallization temperature.
The hot-rolling process typically shapes the steel into various forms and thicknesses. Hot-rolled steel is commonly used in construction and manufacturing applications.
The Benefits of Hot-Rolled Steel
Opting for hot-rolled steel has a lot of advantages. Benefits include:
Quality Performance
The hot-rolling process can refine the grain structure and remove inclusions or other defects. This increases the ductility of the material.
As a result, hot-rolled steel tends to have improved strength and toughness. These improved properties are beneficial for applications where you need high mechanical performance.
Better Workability
Hot-rolled steel has improved workability. The high temperatures during the hot-rolling process make the steel more pliable and easier to form and shape.
Minimal Internal Stress
The gradual cooling process of hot-rolled steel during production helps to minimize internal stresses. As a result, the material is more stable and uniform. This improved stability and uniformity can increase the durability and performance of the final product.
Economical
The hot-rolling process requires less energy as the metal has a lower resistance to deformation at high temperatures. This can result in lower production costs. What’s more, hot-rolled steel tends to be cheaper.
How Hot Rolling Is Done?
The steps involved in the hot rolling process are:
Step 1: Heating
Heat the steel ingots or billets to a temperature above their recrystallization temperature – about 1,700 degrees Fahrenheit or higher.
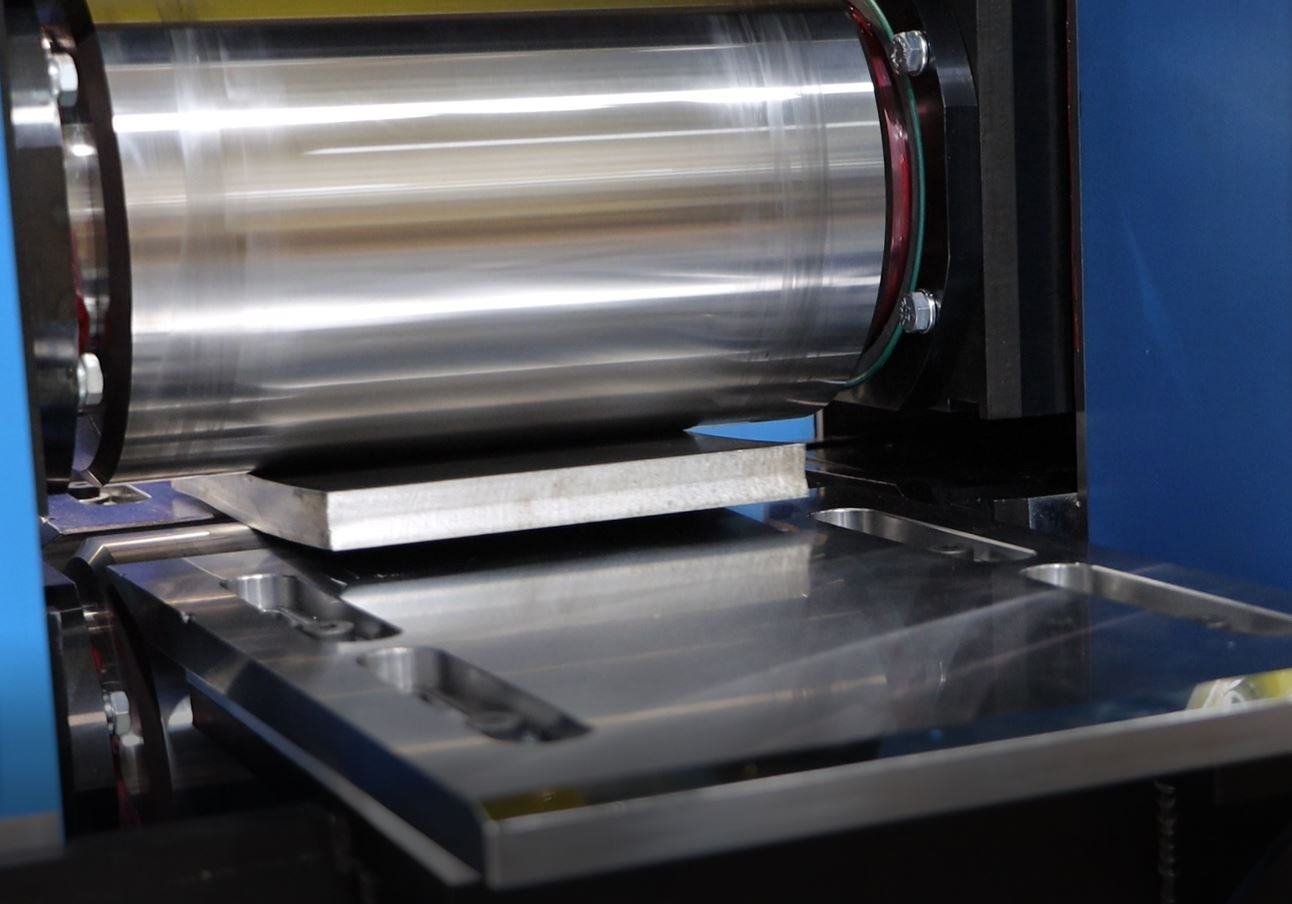
Step 2: Rolling Mill Machine
Pass the heated steel through a rolling mill machine. The machine reduces its thickness and shapes it into the desired form. This process results in increased dimensional accuracy and reduced surface defects.
Step 3: Compression
After shaping the material in the rolling mill machine, it then undergoes compression by a series of rollers. The rollers apply pressure on the steel, reducing its cross-sectional area. This increases the material’s length and decreases its thickness.
Step 4: Cooling
The hot-rolled steel is then cooled using air or water. This helps prevent deformation and reduce its hardness.
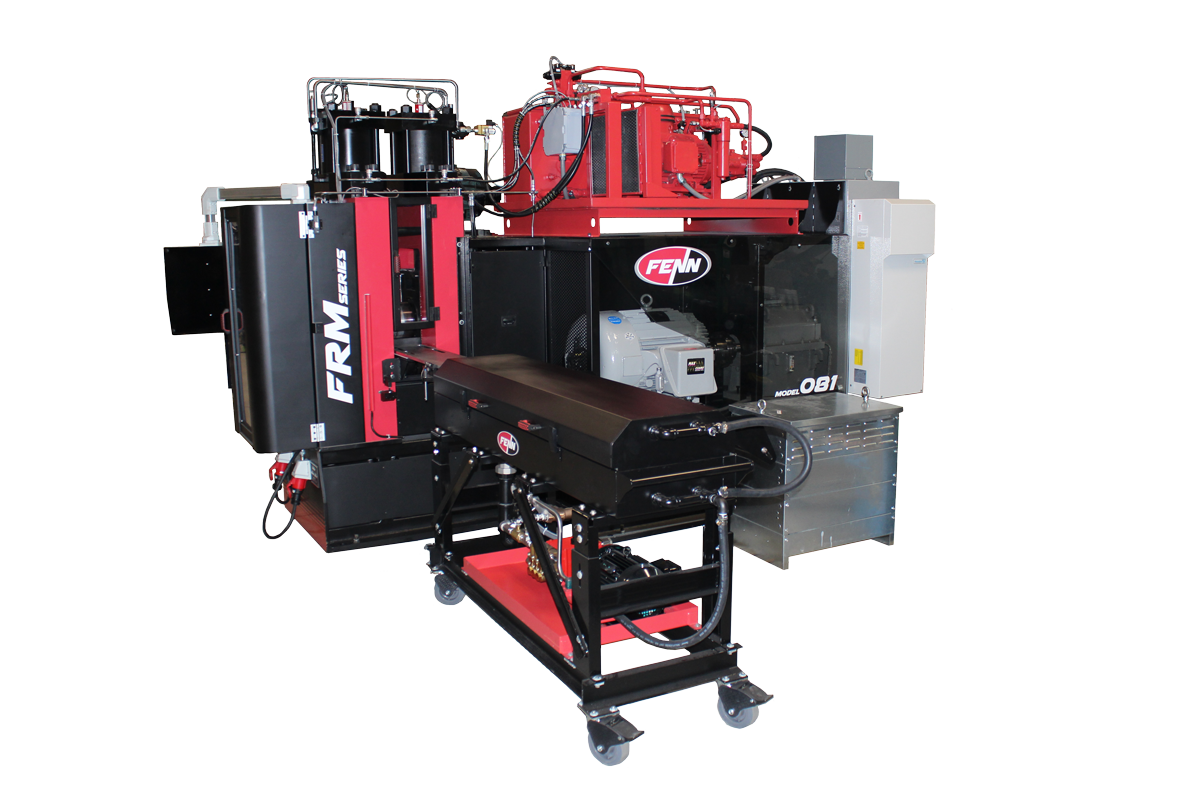
Access High-Quality Hot Rolled Steel
To form quality hot-rolled steel, you need premium hot-rolling mill machinery. At FENN, we engineer and manufacture custom rolling mill machines for various applications. Our goal is to ensure maximum efficiency in your production.
Have a need for a hot rolling mill? With over 120 years as the leading rolling mill manufacturer, we can help design and build the right machine to suit your application requirements. Consult with our experts or get a quote from FENN today! Contact sales@fenn-torin.com.